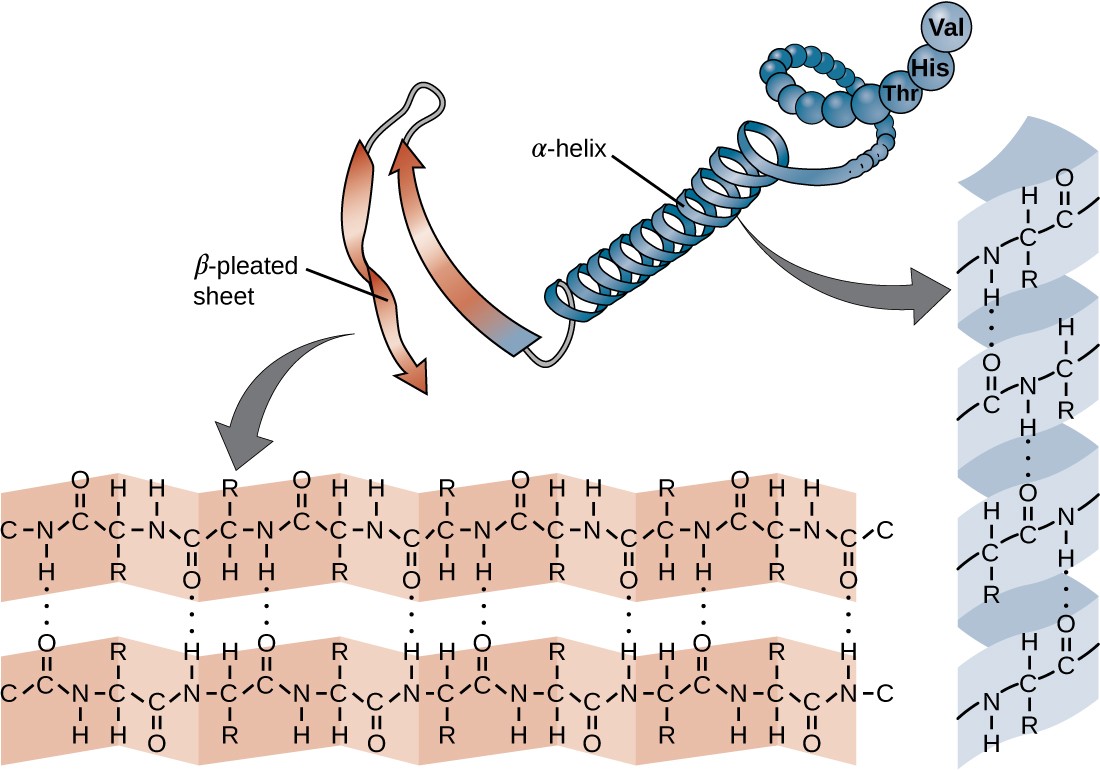
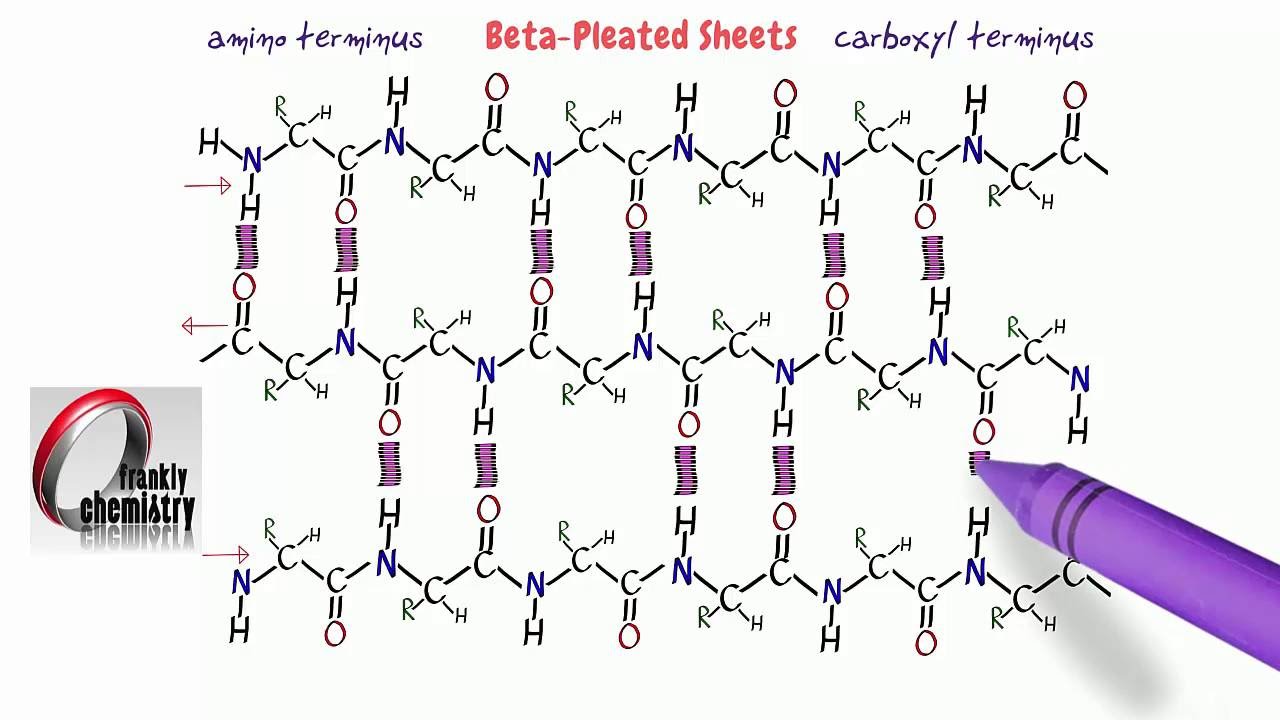
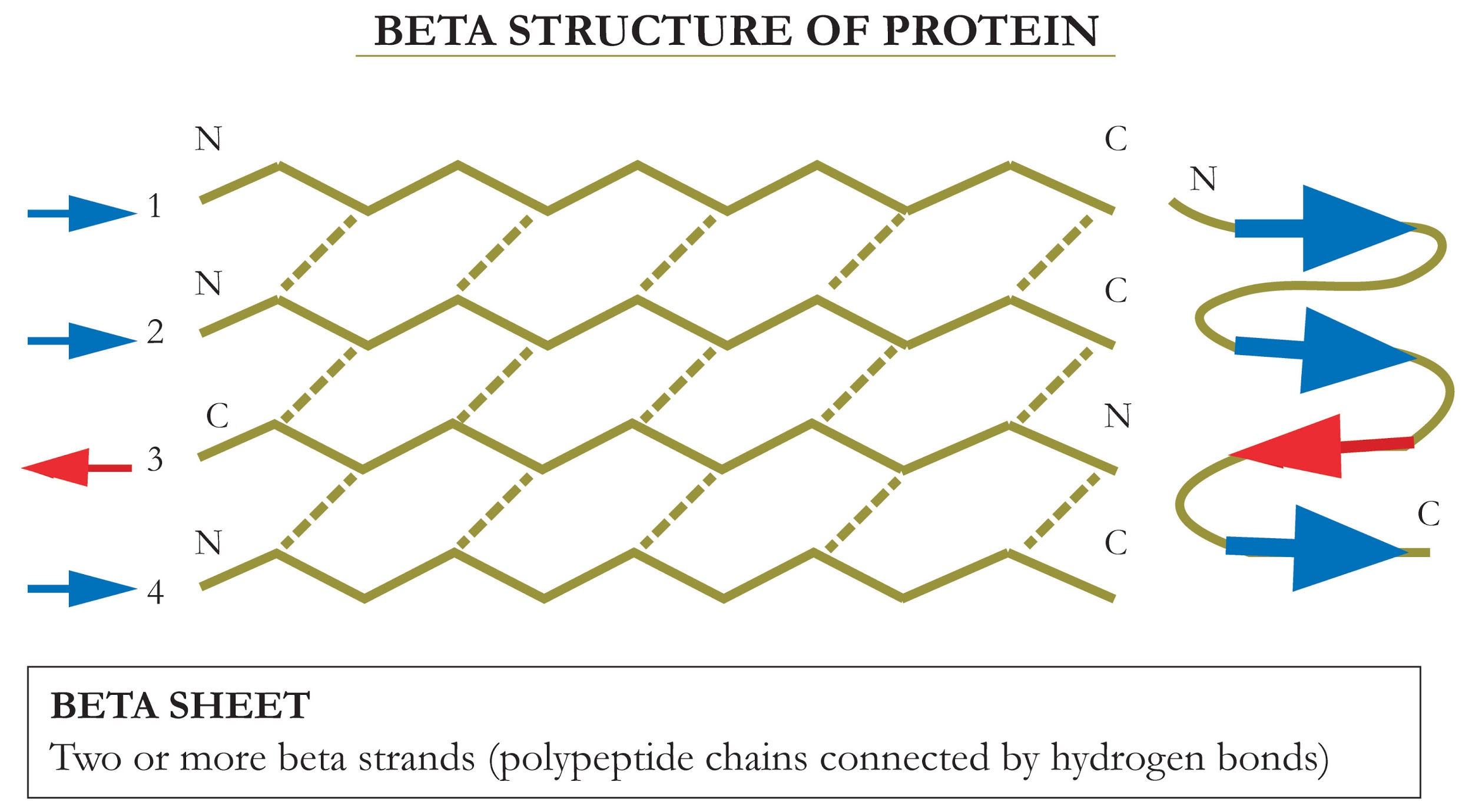
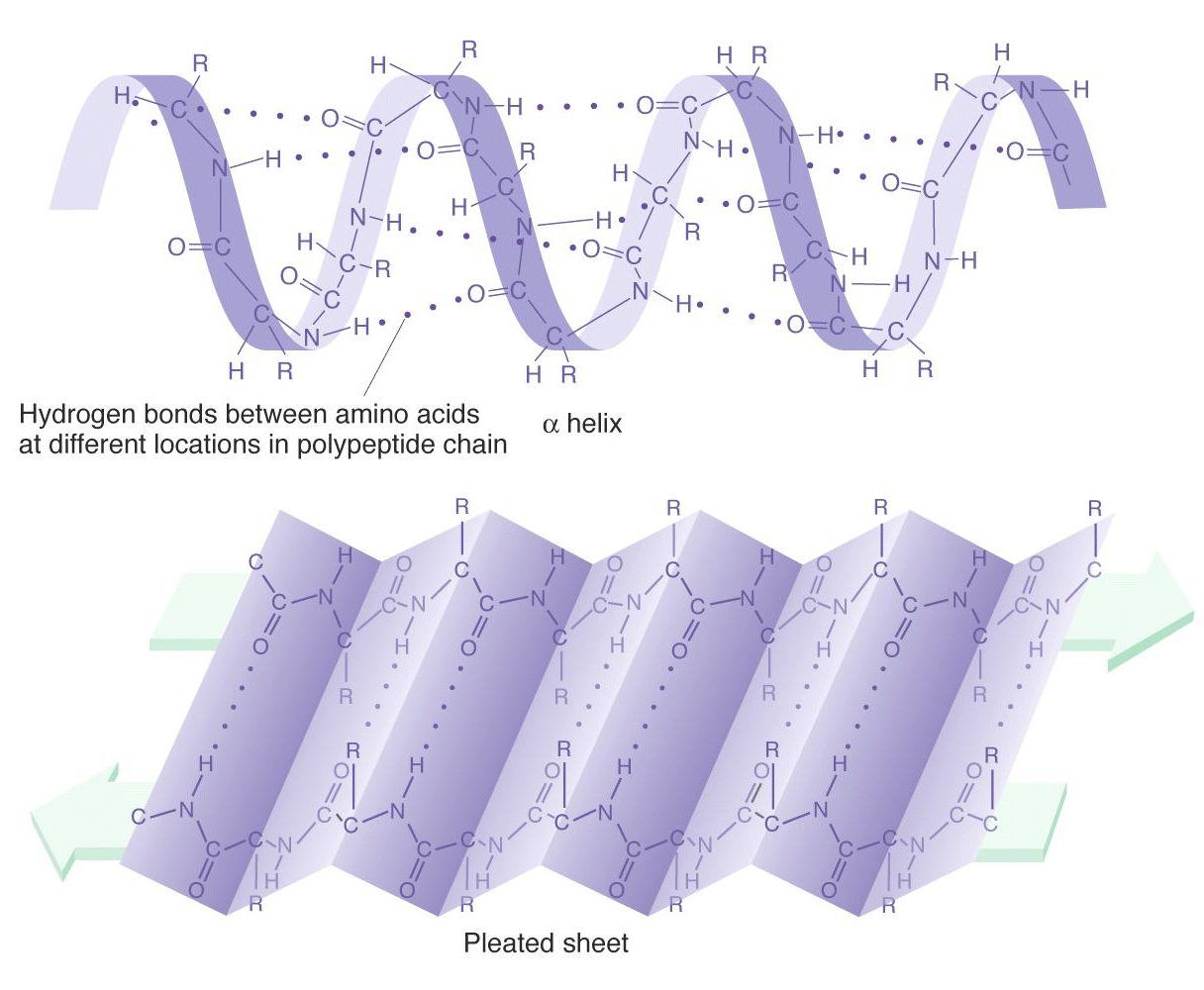
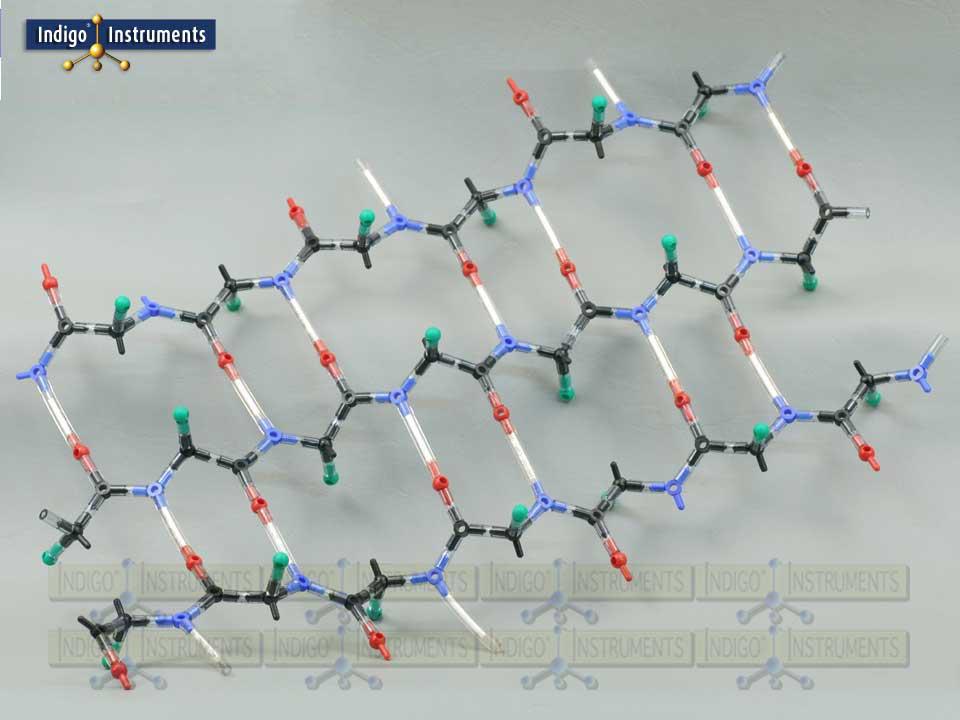
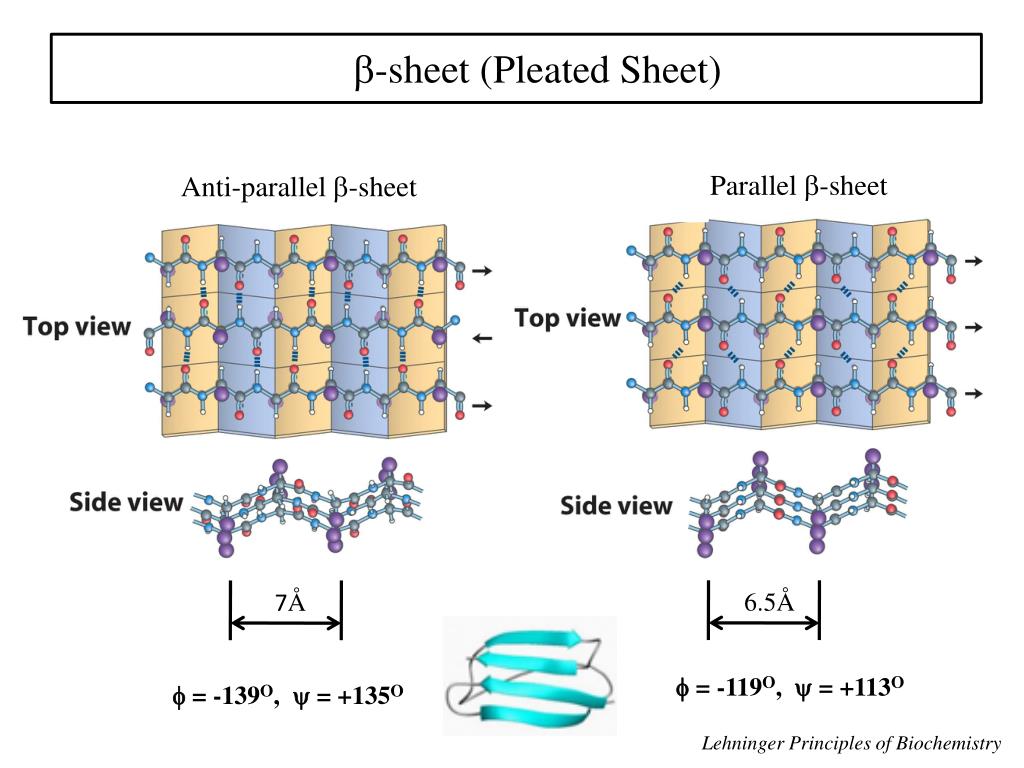
B Pleated Sheet Protein Structure
B Pleated Sheet Protein Structure - The hydrogen bonds form between carbonyl and amino. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Web each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a hydrogen atom.
This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Web each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a hydrogen atom. The hydrogen bonds form between carbonyl and amino.
Web each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a hydrogen atom. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. The hydrogen bonds form between carbonyl and amino.
7.4 Proteins Microbiology 201
Web each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a hydrogen atom. The hydrogen bonds form between carbonyl and amino. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g.
PPT Resource, Materials and Environment PowerPoint Presentation ID
Web each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a hydrogen atom. The hydrogen bonds form between carbonyl and amino. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g.
Amino Acids 8. The betapleated sheets secondary structure of Proteins
This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Web each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a hydrogen atom. The hydrogen bonds form between carbonyl and amino.
The beta pleated sheet structure of protein is due to(a)Formation of
The hydrogen bonds form between carbonyl and amino. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Web each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a hydrogen atom.
MGA2_0325
Web each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a hydrogen atom. The hydrogen bonds form between carbonyl and amino. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g.
Beta pleated sheet Secondary structure of protein YouTube
Web each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a hydrogen atom. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. The hydrogen bonds form between carbonyl and amino.
Pleated Sheet ubicaciondepersonas.cdmx.gob.mx
Web each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a hydrogen atom. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. The hydrogen bonds form between carbonyl and amino.
Secondary structures of keratin protein (beta pleated sheets and alpha
The hydrogen bonds form between carbonyl and amino. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Web each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a hydrogen atom.
PPT Protein Structure PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2128197
This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. The hydrogen bonds form between carbonyl and amino. Web each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a hydrogen atom.
1. Secondary structure of protein, αhelix and βpleated sheet [118
Web each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a hydrogen atom. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. The hydrogen bonds form between carbonyl and amino.
This Structure Occurs When Two (Or More, E.g.
Web each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a hydrogen atom. The hydrogen bonds form between carbonyl and amino.